Home
Lecture 2: Hello World
Learning objective
-
Core concepts
-
Getting started with psql
-
Hello world in SQL
-
SQL style guide
-
Debugging in SQL
Warm up
- ssh into eniac and a lab machine
Core concepts
1. What is data?
Data are individual facts, statistics, or information that are collected for reference or analysis. In its raw form, data itself is useless. However the knowledge underlying the data is of unmeasurable value.
2. What is database?
A database is a (usually large) shared collection of logically related, persistent data used by a set of application systems. The database name is usually a topical description of that data.
3. What is DBMS?
DBMS is short for database management system. It is a set of computer programs that enables users to define, create, and maintain a database and make its information available appropriately. Today, DBMS serves as an interface for users to retrieve information stored in databases. Most DBMS are relational, hence they are also referred to as RDBMS.
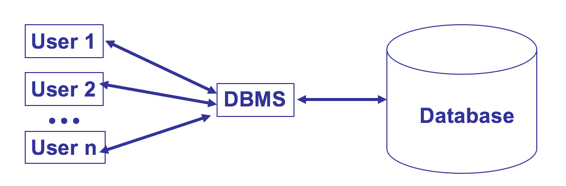
4. What is SQL?
SQL, short for Structural Query Language, is a RDBMS programming language that defines relational constructs (such as schemas and tables) and provide data manipulation capabilities (e.g. data control). SQL by itself cannot create stand-alone programs because it can only be used inside RDBMSs. It is a declarative type of language that leaves the details of implementation (how to do it) to the RDBMS itself.
5. What is a data model?
A model is a representation of reality that retains only selected details. A data model is a notation for describing and organizing data. This includes structure of data, operation on the data, and constraints on the data. There are many different types of data models, for example:
-
hierarchical (tree-oriented) model
-
network (graph-oriented) model
-
relational model (e.g. an entity-relational (ER) model)
-
object-oriented model
-
semi-structured model
6. Basics of a relational model
-
Relational model represents data in a multitude of two-dimensional tables.
-
Each table consists of similar information, stored in columns and rows.
-
Each column of a table are named to describe the data contained in the column (e.g. attributes).
-
The rows of each table contains the values (e.g. tuples).
-
The schema contains the meta information of the table, the columns, and the values contained in the rows.
For more theoretical content, checkout Database Systems The Complete Book (second edition) by Hector Garcia-Molina Jeffrey D. Ullman Jennifer Widom. The content above is referencing the textbook and also adopted with permission from Professors Lei Xie, Di He, and Alvin Lam’s courses.
Getting started with psql
psql is a terminal-based front-end to PostgreSQL (a relational database management system aka RDBMS). It enables you to type in queries interactively, issue them to PostgreSQL, and see the query results.
Exercise:
In your breakout rooms, find the answers for the following questions, using the getting started with psql guide if needed:
-
How many databases are there?
- In the database you are assigned to (see below), how many tables are there?
- Group A: employees
- Group B: dvdrental
- Group C: menagerie
- Group D: shakespeare
-
What is the psql command for
toggle timing of commands? - For the user
instructor, what kind of roles and permissions does this user have?
Hello world in SQL
CRUD and SQL SELECT
CRUD stands for create, read, update, and delete, which are the four major operations implemented by databases.
Mapping to SQL statements, this means:
| CRUD | SQL |
|---|---|
| Create | INSERT |
| Read | SELECT |
| Update | UPDATE |
| Delete | DELETE |
We will be spending the majority of our time with Read, which means SELECT SQL statements.
Writing our first SQL SELECT statement:
-
(optional) navigate to the
employeesdatabase (\c employees) -
(optional) list all tables under this database (
\dt) -
enter into the command line the following SQL SELECT statement:
SELECT *
FROM salaries
;
The basics:
SELECT *
FROM <tablename>
;
-
This SQL query is an example of the most basic building block of a SQL SELECT statement for extracting and reading data.
-
Every SQL query for pulling data must have a
SELECT ...followed by aFROM .... -
The FROM clause tells us the location of the data, aka the table name.
-
The SELECT clause tells us which columns we need from that table.
-
The asterisk (*) (we verbally refer to it as “star”) is a wildcard that is a shorthand for returning all the columns in the table.
There are many different methods of passing a SQL SELECT statement into psql.
-
type directly via command line inside
dbname=> -
open an editor via psql using
\e(e.g. nano, vim, emacs) and type in there -
edit the SQL on your local editor (e.g. Sublime, Atom) and then copy/paste into command line
Exercise:
On your own, run the following SQL SELECT statement using all three methods described above:
SELECT *
FROM employees
;
Hint: to exit out of printing, press q.
SQL style guide
Debugging
Some common SQL syntax errors:
-
Did you spell the table name correctly?
-
Did you include a semi colon at the end of the SQL statement?
-
Did you spell the SQL reserve keywords correctly? (a good text editor can help you with this)
-
Did you preserve the order of
SELECT .... FROM ...?
Order of debugging
One interesting thing to note is that SQL debugger will only return the error message for the first error it encounters. If you fix that error, then and only then, the second error in the same SQL statement will be printed. Although we write the SQL statement in the order of SELECT ... followed by FROM ..., SQL actually evaluates the FROM ... clause first.
Exercise:
On your own, debug the following SQL SELECT statement inside the employees database and fix all the errors until it correctly runs:
SLECT *
FROM title
Wrapping up
- Homework 1 due on Gradescope this Wednesday.
- Homework 2 will soon follow.
- Any set up issues?